The following examples illustrate how molecules are built in GaussView. As some of the tutorials build on previous material, be sure to save each file when finished.
Building Pyridine: Using Untyped Atoms

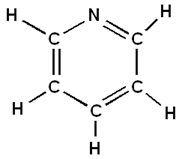
The following is an example of how Pyridine is built in GaussView:
1. Start a new file by selecting the New=>Create Molecule Group option from the File menu in the main window.
2. Click on the Rings icon on the Builder window; this makes Rings your "current fragment" as a ring structure appears in the main window.
3. Click on the Rings icon again; this opens the Ring Fragment palette. Select benzene from the ring fragments; a benzene molecule appears in the Current Fragment window. (Alternatively, you can select benzene from the drop-down list in the main window.)
4. Return to the View window. Click once: benzene displays.
5. Double-click on Element on the Builder window to open the Element Fragment palette. Click on nitrogen to select it.
6. Click on the "hot" atom in the Current Fragment display; a nitrogen atom appears.
 Do not select one of the hybridizations. It is usually easier to use untyped atoms.
Do not select one of the hybridizations. It is usually easier to use untyped atoms.
7. In the View window, click on the carbon atom you want to change to nitrogen.
8. Select the Delete Atom button on the Builder window.
9. On the View window, delete the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen by clicking on it.
10. Click on the Rebond button on the Builder window, then click on the Clean button.
 You will often want to rebond before cleaning.
You will often want to rebond before cleaning.
Pyridine is now complete. Save your work.
Building Phenylpyridine: Setting the Angle Between Rings
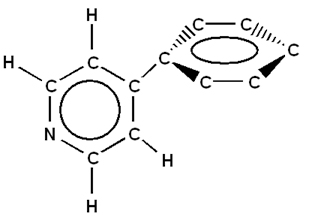
This example shows how to build Phenylpyridine based on an existing file, in this case, Pyridine.
1. We will be continuing from the previous example, Building Pyridine.
2. Double-click on Rings on the Builder window. Be sure that the phenyl ring is selected.
3. Click on the hydrogen atom located on the carbon atom opposite the nitrogen atom on the View window. A second ring is attached to the first ring in place of the hydrogen.
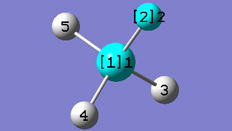
4. Select the Dihedral button on the Builder window.
5. Select atoms between the two rings, as shown in the following figure:
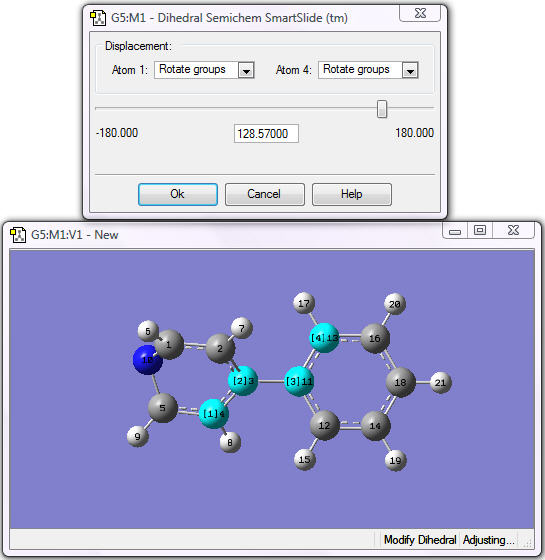
The SmartSlide window opens when four atoms have been selected; make sure that Rotate Groups is selected for both Atoms 1 and 4.
Modifying the Dihedral Angle
6. Move the slider to create a dihedral until the rings are perpendicular to each other (or enter 90.0 in the text box).
7. Click on the OK button.
Phenylpyridine is now complete.
Building Iron Pentacarbonyl: Selecting the Best Templates for a Given Task
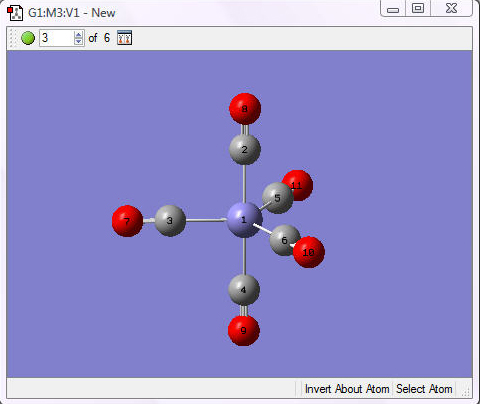
This example builds iron pentacarbonyl.
1. Start a new file by selecting the New=>Create Molecule Group option from the File menu in theView window. Select the element iron and then choose the trigonal bipyramidal iron template:

2. Return to the View window. Click once: the iron molecule displays.
3. Double-click on R-Group on the Builder window to open the R-Group Fragment palette. Select the linear C-N template and place this group on each bond to the iron atom. Note that we select this template rather than one of the C-O groups because the former is linear.
3. Change the nitrogen atoms to oxygen atoms: select the element oxygen and then the free atom template (using either the choices at the bottom of the Element Fragment palette or the drop-down list on the main screen).
The molecule is now complete.
Building Tyrian Purple Dye: Appending a Structure
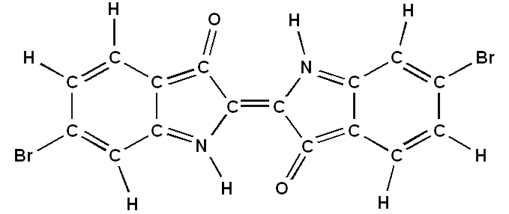
The following is an example of how a Tyrian purple dye 6,6'-dibromoindigo is built in GaussView:
1. Create a new file. Double-click on Rings on the Builder window to open the Ring Fragment palette.
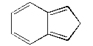
2. Select the fused 5 and 6 carbon rings on the Builder window (see illustration immediately above) then click on the View window to place a fragment.
3. Select the oxygen element and change the appropriate hydrogen atom in the five-member ring to oxygen by clicking on it.
4. Change the carbon atom opposite the oxygen to nitrogen.
5. Change the hydrogen atom on the outermost carbon atom in the six-member ring (on the same side as the nitrogen) to bromine in a similar manner.
6. Select Clean on the Builder window. Do not rebond. Save the file.
7. Append the file you just saved to the display on the View window: copy the file to make it appear in the Current Fragment window, then click in the View window to paste the current fragment.
8. Rotate and move the second ring so that the two carbon atoms to be bonded are close together, and the two fragments are oriented properly with respect to one another.
 To affect just one of the two fragments, hold down the Alt key while dragging the mouse. Using a second window is often helpful when performing complex positioning operations. Use the Add View option on the View menu to create one.
To affect just one of the two fragments, hold down the Alt key while dragging the mouse. Using a second window is often helpful when performing complex positioning operations. Use the Add View option on the View menu to create one.
9. Delete the hydrogen atoms on the two carbon atoms to be bonded.
10. Create a double bond between the two carbon atoms: select the Modify Bond icon on the Builder window, then click on the two carbon atoms to be bonded. The SmartSlide window opens; choose the double bond option from the Bond-Type list and click OK.
11. Click on Clean.
The 6,6'-dibromoindigo molecule is now complete. Save your work.
Docking Two Structures: Building Bichloro-Diphenyl
This example illustrates a method for building a molecular structure consisting of docked framents.
1. Create a new View window and place a benzene ring in it. Change one of the hydrogen atoms to Chlorine. Repeat this process to create a second chlorobenzene ring.
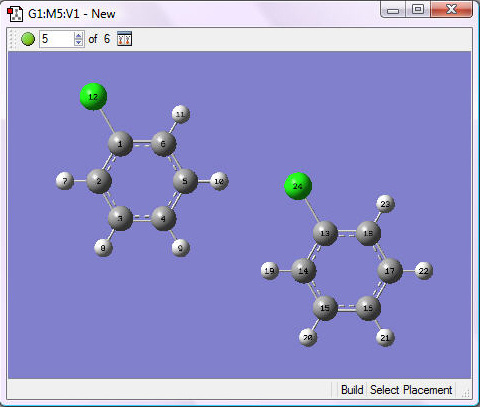
2. Rotate one of the rings so that the chlorine atom is in the opposite position to the one in the first ring. You can accomplish this by holding down the Alt key while holding down the left mouse button and dragging:
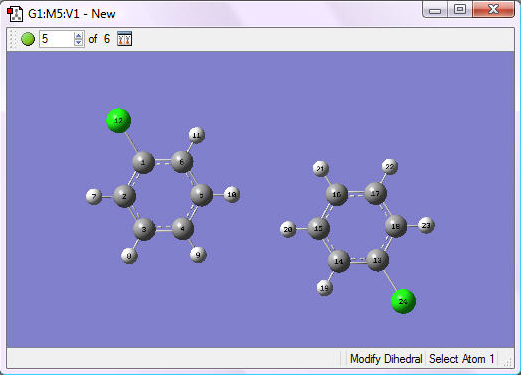
3. Position the rings so that they overlap and the carbon atoms to be bonded are in correct position:
4. Delete the hydrogen atoms and dangling bonds in the overlap region.
5. Create a bond between the two carbon atoms, completing the molecule:
6. Click on Clean; the molecule is now complete.
Assigning Atoms to ONIOM Layers in a Small Peptide Chain
Note: This example is devised for its illustrative clarity rather than for scientific interest. Your molecule may look different from the figures below.
1. Create a peptide chain containing these amino acids: Phe-Ala-Gly: use the Biological Fragment palette to choose an Amino-Terminal Phenylalanine, a Central Fragment Alanine and a Carboxyl-Terminal Glycine, placing each in the same View window and bonding them as shown previously in this tutorial.
2. Assign all atoms to the Low Layer. Choose Select Layer from the Edit menu, and then click Select All. Verify that current layer is set to Low. The display will look similar to the following figure.
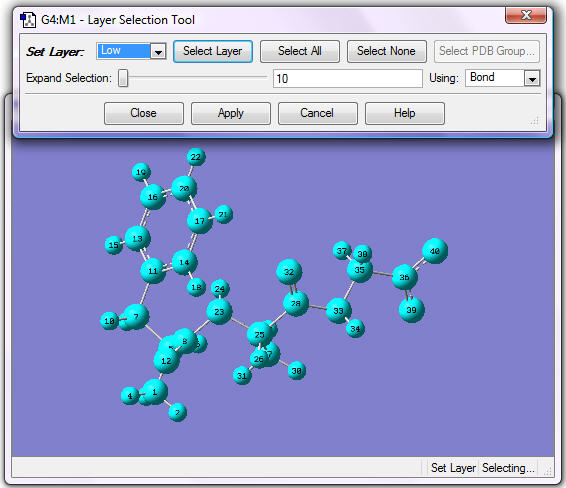
Click Apply.
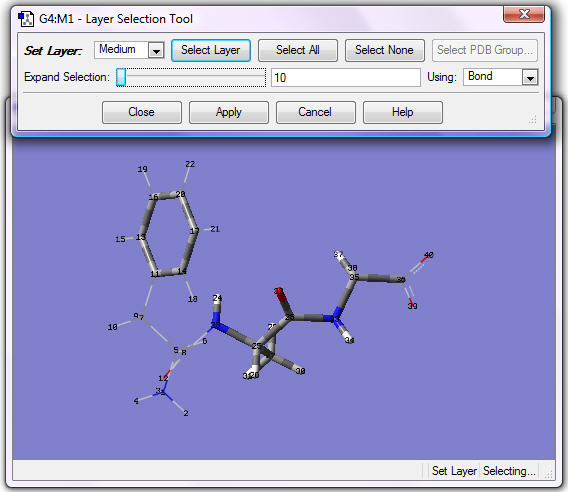
3. Assign the following atoms to the Medium layer: all atoms in Ala, carbons in Ring in Phe and atoms up to the double bond in Gly. Use any selection method you want; it will usually take two or more operations to assign all these atoms. For example, you can select the central carbon atom in Ala and drag the Expand Selection slider to add more atoms. Adding too few atoms is usually easier than adding too many. Click Apply.
Add additional atoms as necessary (use the center mouse button [or Shift+Click] to select, then click Apply) until the selection is correct as in the following figure. The atoms in the Medium layer are now displayed as tubes and the ones in the Low layer are in wireframe in the display:
4. Assign the following atoms to the High layer: all atoms in Ala, including heavy atoms bonded to them. One selection method is to click the central carbon in Ala, change Using field to Distance, and click twice at the right end of Expand Selection. The display will be as in the following figure:
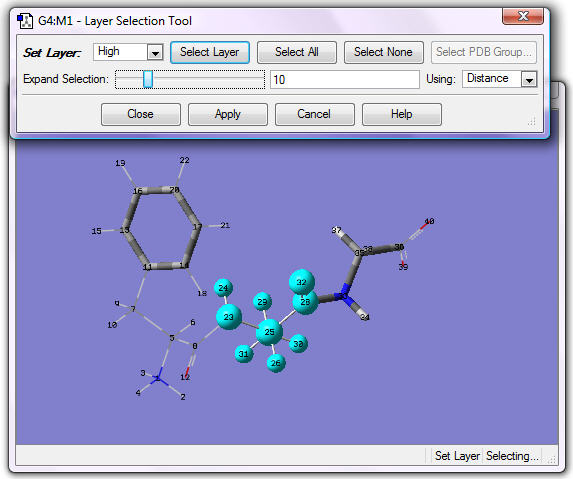
Click Apply. The display is as in the following figure:
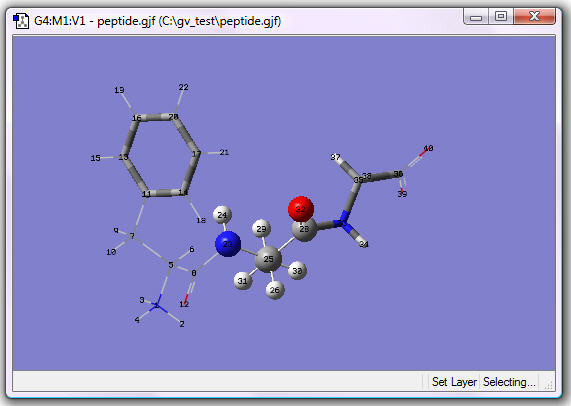
Completed ONIOM-Assigned Molecule
Remove the hydrogen atom that was just placed into the high layer by selecting it and then placing it in the Medium layer.
Click Close.
The atom layer assignment is now complete. Save your work.
Setting Up an ONIOM Job
This example uses the molecule that was built and the layers that were defined in the final example in the Building Tutorial, and it continues on from those steps.
1. Select Gaussian Calculation Setup from the Calculate menu.
2. On the Method tab, check Multilayer ONIOM Model. Three tabs appear (High, Medium, and Low) in the Method section, which you can use to select the methods for treating each layer of atoms.
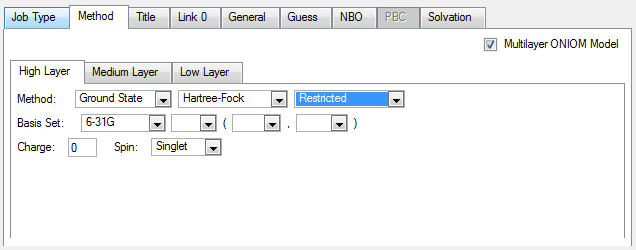
3. Click on the High tab, then select an RHF/6-31G job:
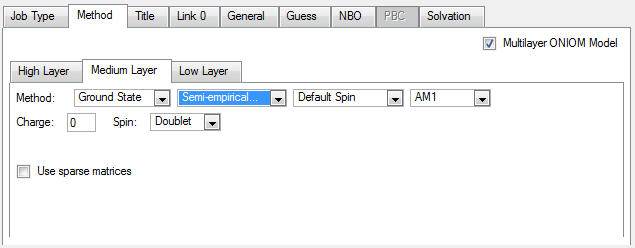
4. Click on the Medium tab, then select an AM1 job:
5. Click on the Low tab and specify a molecular mechanics calculation using the Amber force field:
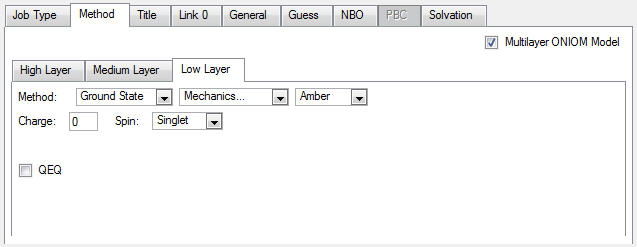
6.
These settings place the following line in the job's route section:
# ONIOM=(RHF/6-31G:AM1:Amber)
You can now go on to fill out the rest of the dialog box, and the job will be ready to be saved and run.