Maxwell went beyond simply predicting the average speed for a sample of gas particles to developing an expression for the distribution of speeds. This expression is used in the applet below and the program allows you to visualise the distribution of speeds in a model gas sample.
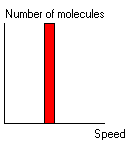
When the model is initialised a sample of 100 gas particles are set up and all given an initial speed equal to the average speed for the mass of the model particles and the absolute temperature of the model:

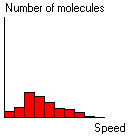
The resulting distribution of speeds has been experimentally confirmed along with Maxwell's theoretical prediction that the average speed is slightly greater than the most probable speed for the gas particles.