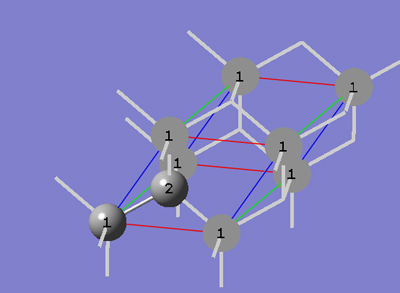
Periodic Boundary Conditions (PBC)
Tutorial 6 - Transform a Face-Centered Unit Cell of Diamond Crystal to a Primitive Unit Cell, PBC/3D
6-1 Follow steps 4-1 through 4-8 of PBC Tutorial 4, then do the following steps: (a) uncheck the Enable Space Group Symmetry box in the Symmetry tab; (b) select Fix Contents' Cartesian Coordinates from the Cell Changes drop-down list of the Cell tab.

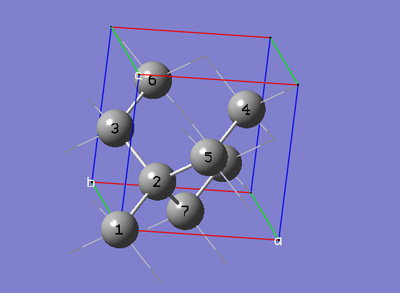
6-2 In the Cell tab of the PBC dialog, push down the Place button and select a (1,0,0) instead of 0 (0,0,0) to enable placement of the head of the "a" lattice vector at any atom selected in the view window using the mouse. In the view window, click on atom 7.
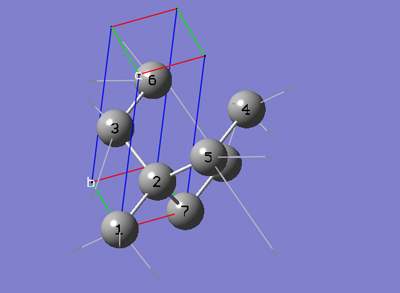
6-3 In the Cell tab of the PBC dialog, push down the Place button and select b (0,1,0) instead of a (1,0,0) to enable placement of the head of the "b" lattice vector at any atom selected in the view window using the mouse. In the view window, click on atom 3.
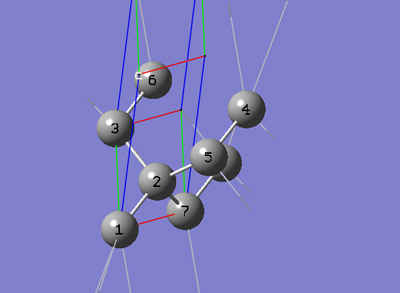
6-4 In the Cell tab of the PBC dialog, push down the Place button and selectc (0,0,1) instead of b (0,1,0) to enable placement of the head of the "c" lattice vector at any atom selected in the view window using the mouse. In the view window, click on atom 5.
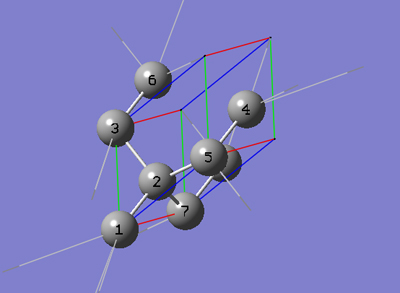
6-5 In the Cell tab of the PBC dialog, select Delete All Atoms Outside Cell from the Trim Contents popup menu.
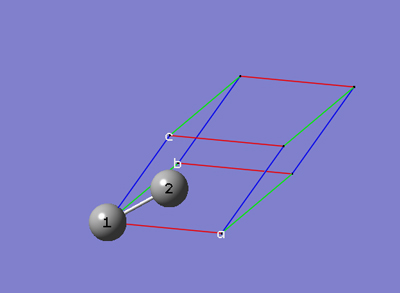
6-6 In the Contents tab of the PBC dialog, select Rebond All from the Bonds popup menu.
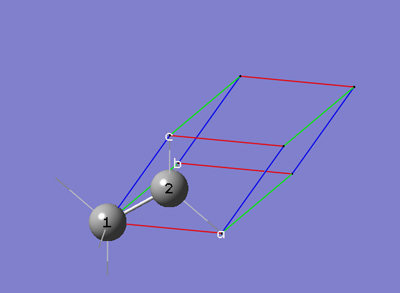
6-7 In the View tab of the PBC dialog, select Dull from the Replicate Contents Display drop-down list.
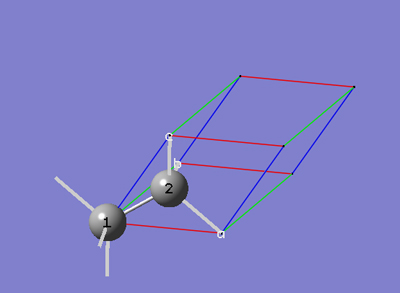
6-8 We now have a primitive unit cell for diamond crystal which gives the same crystal structure as that from the face-centered cubic unit cell we started with.
6-9 In the View tab of the PBC dialog, check the "Show All Boundary Atoms" checkbox.